- +1.888.528.8757
- office@doctorspreferredhhc.com
- Monday – Friday 9 AM – 5 PM
Have you ever heard the most-used phrase “Movement is life!”? It’s true but it’s even significant for millions of people with joint pain. And joint diseases in the elderly are taken for granted. As a rule, if there is pain, people write them off as they are approaching old age. But what are the causes of joint diseases in the elderly? How to treat them? Is it possible to prevent or slow down the development of joint diseases? Let’s check it out together.
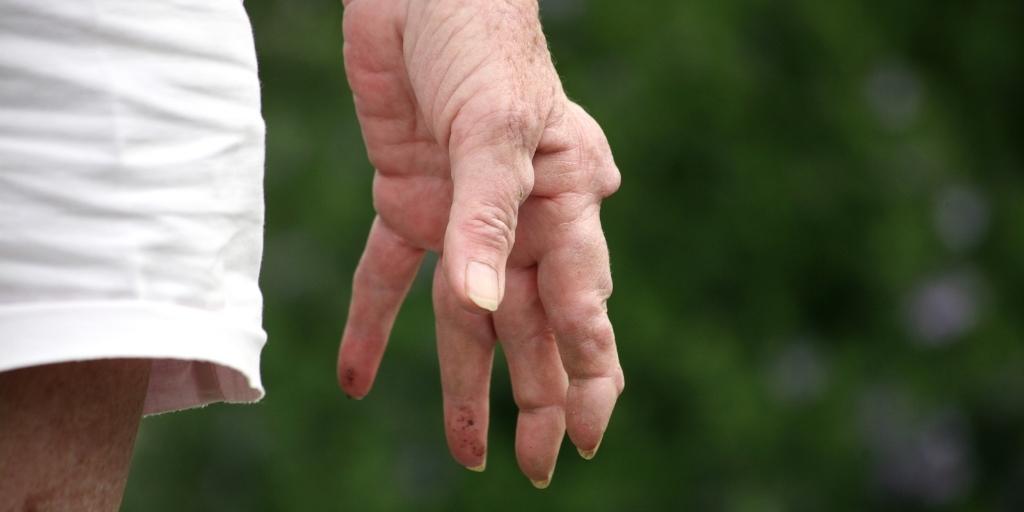
How common are joint diseases in the elderly? The joint is the junction of the bones, it is a kind of cavity with articular fluid, which serves to reduce friction between the bones. It is the joints that help a person to make all the movements. As long as our joints are healthy, we do not notice their work. Only over the years, faced with unbearable pain when walking, squatting, or climbing stairs, do we begin to appreciate them. Joint diseases in the elderly are often irreversible and chronic.
Restriction of freedom of movement due to pain is very common especially among the elderly. Impartial statistics speak of terrible figures; almost all elderly people over 75 have joint problems. And at the age of 65, nearly 75% of them are already concerned about the symptoms of the disease. It is quite obvious that joint diseases in the elderly occur against the background of age-related changes, namely joint modifications, muscles, and tissues. In addition to natural aging, there may be other reasons to strengthen the disease or accelerate the exacerbation.
Having established the diagnosis, it is necessary to determine the causes of pathology as the nature of treatment depends on it. It is difficult to say how this or that disease has developed. With age, the musculoskeletal system of a person undergoes significant changes. In old age, the volume of muscle mass changes, because muscles without intensive physical work become flabby and atrophied. Cartilage is no longer so elastic and even gets thinner.
The etiology has not been disclosed yet. Among the causal factors of aging, the latest research has mentioned staphylococci, group B streptococci, and their other forms as well as Yersinia Enterocolitica as the main causes of arthritis.
Currently, the immunosuppressive theory has become the most widespread. According to it, when rheumatoid arthritis occurs, a hereditary anomaly of the immune system is assumed. The role of hereditary factors in the development of rheumatoid arthritis is also confirmed by such facts as the high frequency of simultaneous disease of monozygotic twins, and the high frequency of the disease in close relatives of patients.
Another cause of developing arthritis is the endogenous nature of an individual. The external influences such as flickering, injuries, and interethnic diseases also matter.
In most cases, the onset of arthritis results in severe complications that endanger your health, ability to work, and motor activity.
Among these complexities are:
And as of recent medical research, the development of these pathologies and complications has been growing rapidly in recent years. If not treated in the right way and on time, the inevitable pathological processes will take place in your body and will lead to irreversible destructive changes in joints.
The main way you can reduce the chances of developing arthritis is to avoid using products that contain tobacco, be at your normal weight, and dry to avoid injuries.
As mentioned above, one way of preventing arthritis is to control your weight. Your knees should be able to support your body. In this case, doing regular exercises can also reduce the risk of arthritis. Recommended types of exercises are stretching, swimming, walking, etc.
And, of course, consult your doctor on time. The best treatment is prevention.
At first, rheumatoid arthritis scares patients. Whenever they hear an accurate diagnosis, many patients fall into depression. Modern medicine does not know how to explain the causes of the disease, offer effective prevention of the disease, or guarantee patients that they will completely get healed. However, it is unacceptable to fall into despair. It is crucial just to consult a doctor and get to know to-dos.
The absence of a guarantee of complete healing does not mean a complete deterioration of the conditions of activity. To optimize the quality of life, patients with rheumatoid arthritis should follow some basic recommendations;
First of all, most patients are concerned about how long the disease will allow them to live normally. Life expectancy in rheumatoid arthritis is due to a combination of various factors such as how fast you consult a doctor, monitoring the health, genetics, etc. This affects at first mental health. And the answer to the above-mentioned question is simple; treat the disease easily. Keep in mind that rheumatoid arthritis does not belong to the category of diseases with mandatory fatal outcomes. Proper treatment of the disease, consultations with medical recommendations help to interact and live your life to its fullest.