- +1.888.528.8757
- office@doctorspreferredhhc.com
- Monday – Friday 9 AM – 5 PM
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a respiratory system inflammation that makes it difficult to pass air through the bronchi and restricts the passage of oxygen into the lungs. Respiratory failure develops, as a result, evidenced by shortness of breath. The more advanced the stage of the illness, the more shortness of breath a person has. It’s especially bad while you’re moving about or doing strenuous labor. Although a person cannot be totally cured, long-term remission can be achieved with lifestyle adjustments and supportive therapy.
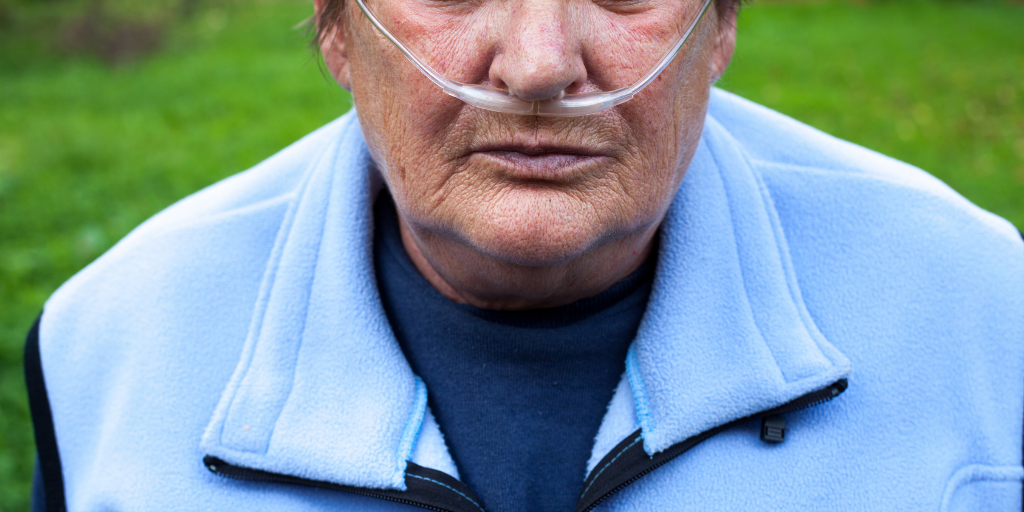
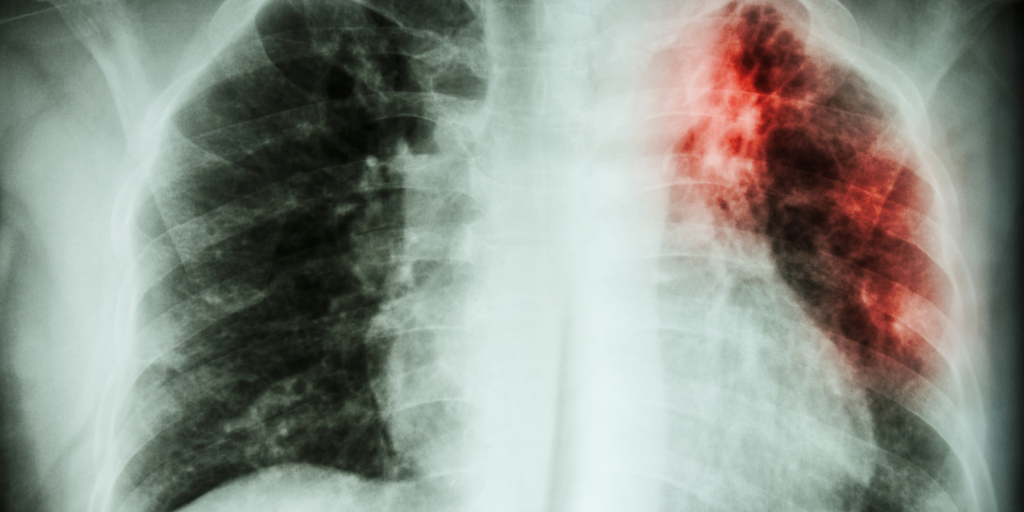

Lung tissue is slowly damaged over a lengthy period of time, often without causing any symptoms. As a result, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is most commonly diagnosed in adults over the age of 60-65. People with a history of major infectious lung infections, particularly those who endured them as children, are at a higher risk of developing COPD. Patients with emphysema of the lungs aged 30-40 years are occasionally identified with a genetic abnormality of the alpha-1-antitrypsin protein.
COPD aggravations contribute to the pathogenic process’ development. Infectious agents such as hemophilia bacillus, pneumococcus, and gram-negative Enterobacter are the most common causes of aggravation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Chronic inflammation is a major factor in the progression of COPD. In the early phases of chronic obstructive pulmonary illness, the inflammatory process of the respiratory tract is already evident.
Tobacco smoking is another major cause of COPD. Smoking has been misused by 90% of the patients. When you smoke, carbon monoxide, nicotine, and tobacco resins enter your lungs, producing an environment that encourages mucus production. All of this contributes to the disease’s progression. Passive smokers, or those who inhale cigarette smoke on a regular basis, are also in danger.
Working in hazardous sectors may contribute to the development of COPD. Hazardous industries are those in which workers are exposed to chemicals, coal dust, toxic impurities, and other pollutants, as well as air pollution from mineral dust, gas, and smoke. Metal grinders, miners, those who work in the paper sector, and people who work in agriculture are the most likely to contract the illness.
Despite the fact that COPD is not a genetic disease, you are at a higher risk if you have close relatives who have it.
Coughing is the most visible indicator that COPD is progressing. Cough may be episodic at first, but as time passes, it begins to bother the patient on a daily basis. Coughing from a smoker might be a sign of obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
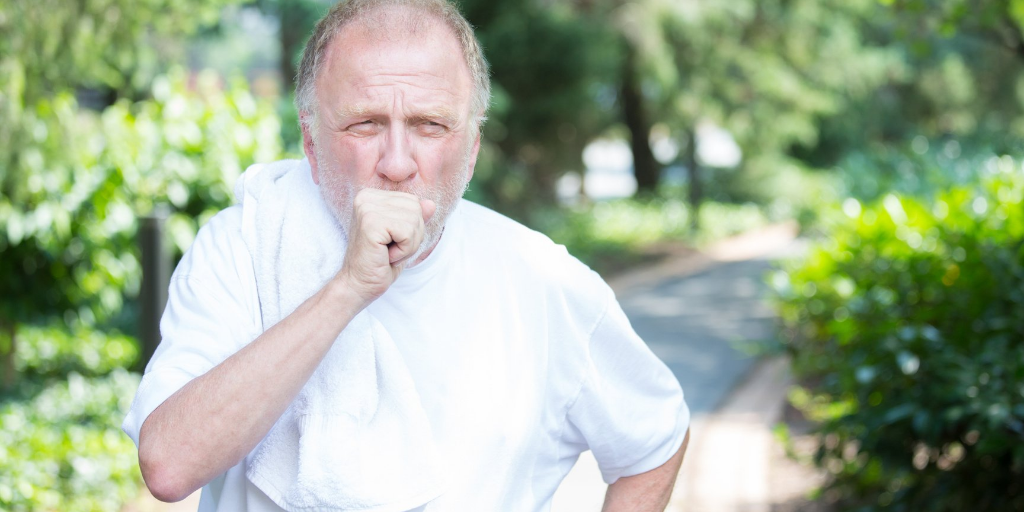

Other symptoms might include:
The patient’s complexion develops a bluish hue, puffiness, and other symptoms as respiratory insufficiency progress. Carbon dioxide poisoning symptoms may appear in advanced types of the disease.
The goal of therapy for the stable obstructive pulmonary disease is to prevent aggravations and improve respiratory system functioning. A variety of methods are used, including tobacco refusing, inhalation, oxygen treatment, and so on.
Surgical intervention is required in some states. In order to minimize problems, patients with COPD are advised to acquire an influenza vaccination.
It’s highly advisable to care about your health before you run into any complications.